🔬 First lab#
💻 Work environment setup#
⏱ Expected work time 30 minutes
To follow the course effectively, you will need to set up your local development environment to interact with the course materials and to write&run code examples.
Follow the instructions and helpful info on a separate page Work environment setup
Setup your local evnironment before proceeding with this lab. Checklist:
☑️ Install Anaconda Python distribution
☑️ Install a good text editor (e.g. VSCode, Sublime Text, Atom, etc)
☑️ Install Git and Git GUI
☑️ Register at GitHub
🛠 Task 1.1: Git and Github#
⏱ Expected work time 30 minutes
In this task you practice using Git and GitHub to be able to follow the course coding examples and submit your work for assessment.
Perform the following steps:
☑️ Find the course exercises repository at
https://github.com/fediskhakov/UiO2026_course_code☑️ Follow instructions in GitHub documentation and fork the repository to your own GitHub account
☑️ Continue with the instructions to clone the forked repository to your local machine using Git GUI
☑️ Continue with the instructions to create a Git remote named
upstreamthat points to the original repository. This will allow you to sync your fork with the original repository later on as the course progresses☑️ Make a copy of the file
lab1/survey/questionnaire.mdintolab1/survey/survey_[yourlastname].md(replace with your actual last name) and answer the questions in the copied file☑️ Commit the changes to your local repository using Git GUI
☑️ Push the changes to your forked repository on GitHub and verify that the file
survey_[yourlastname].mdappears in your forked repository on GitHub website☑️ Follow the instructions in GitHub documentation to create a Pull Request from your forked repository to the original upstream repository to submit your answered questionnaire
🛠 Task 1.2: Evaluating polynomials#
⏱ Expected work time 20 minutes
This and the next few tasks are designed to remind you of and get your hands dirty with some Python coding. Feel free to use AI tools such as ChatGPT to help you with coding, but make sure you understand every line of the code you write.
☑️ Study the preliminary code provided in
lab1/poly_pre.ipynbJupyter notebook☑️ Complete the code using the hints provided in the comments
☑️ Run the code in the notebook to test your implementation with different polynomials and input values
☑️ Compare the two implementations in terms of performance using the
timemodule ortimeitmagic in Jupyter notebook, as explained in the notebook☑️ Reflect on the results and write a short summary of your findings
Why do we have to care about the run time of the numerical code?
🛠 Task 1.3: Towers of Hanoi#
⏱ Expected work time 20 minutes
Here we implement a classic recursive algorithm to solve the Towers of Hanoi problem using recursion and while loop.
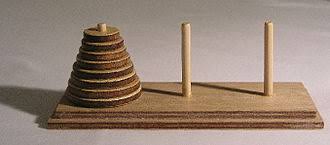
Classic puzzle:
given a board with three pegs,
move a stack of disks of different size from the left-most peg to the right-most peg,
moving one disk at a time and following the rule that
no larger disk can be place on top of a smaller one.
Can a program call itself? Does that make sense and is it useful?
☑️ Study the problem and preliminary code provided in
lab1/hanoi_pre.ipynbJupyter notebook☑️ Complete the code using the hints provided in the comments
☑️ Run the code to test your implementation with different number of disks (and physical props if available)
🛠 Task 1.3: Binary search and bisections solver#
⏱ Expected work time 40 minutes
In this task you study two fundamental algorithms for quick searching a sorted array and for finding roots of continuous functions with alternating signs on an interval. Both algorithms have \(\log(n)\) complexity and are based on the same idea of divide and conquer which we will discuss, along with the alternative algorithms to solve the same problems.
Binary search is finding a discrete element in a sorted list.
Example
Think of number between 1 and 100
How many guesses are needed to locate it if the only answers are “below” and “above”?
What is the optimal sequence of questions?
Explain the operation of the algorithm below. Is this quicker than direct enumeration?
Inputs: sorted list of numbers, and a value to find
Algorithm:
1. Find middle point
1. If the sought value is below, reduce the list to the lower half
1. If the sought value is above, reduce the list to the upper half
☑️ Study the preliminary code provided in
lab1/binary_search_pre.ipynbJupyter notebook☑️ Complete the code using the hints provided
☑️ Run the timing code in the notebook. How does the runtime changes as the size of input grows?
☑️ Repeat the same steps for the bisections solver
🛠 Task 1.4: Newton-Raphson solver#
⏱ Expected work time 20 minutes
Bisections methods is a very robust solver (when it is applicable) but there is a much faster way to solve equations – Newton-Raphson algorithm and its generalizations used for:
Equation solving
Finding maximum/minimum based on solving FOCs
In this exercise you study the algorithm and its implementation, and compare the rates of conversion between bisections and Newton solvers.
Derivation for Newton method using Taylor series expansion#
Searching for \(x\) that satisfied \(f(x)=0\).
Take first two terms, assume \( f(x) \) is solution, and let \( x_0=x_i \) and \( x=x_{i+1} \)
The main ides of Newton-Raphson method is to iterate on the equation starting from some \(x_0\)
Applicable to the system of equations, in which case \(x\in\mathbb{R}^n\) and \(f: \mathbb{R}^n \to \mathbb{R}^n\)
Algorithm is given by
Input: function f(x)
gradient function f'(x)
Algorithm:
1. Start with some good initial value
2. Update x using Newton step above
3. Iterate until convergence
☑️ Study the preliminary code provided in
lab1/newton_pre.ipynbJupyter notebook☑️ Implement the Newton-Raphson method for finding roots of a continuous function
☑️ Run the example to demonstrate the work of the algorithm
☑️ Using the callback feature, display the relative errors on each iteration
☑️ Compare convergence rate to the bisection method
Should we always prefer Newton-Raphson method over bisections? Could you guess/investigate what issues it may suffer from?
🛠 Task 1.5: Multinomial logit model#
⏱ Expected work time 40 minutes
This is the main practical task of the lab, now that we are done with the preliminary exercises.
☑️ Follow instructions in the notebook
lab1/logit_pre.ipynb
We will finish this code in the second lab, you are also welcome to carry out the implementation as a homework.